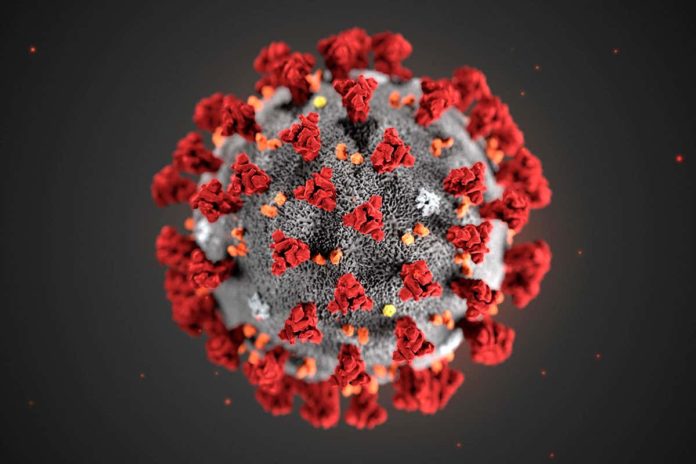
According to the WHO report the recovery time for the coronavirus disease is from 2 week to 6 weeks. The patients with mild cases recover in approximately 2 weeks. In case of severe or critical disease it may take 3-6 weeks for the recovery of patient from Covid-19 infection.
According to the WHO statement “Using available preliminary data, the median time from onset to clinical recovery for mild cases is approximately 2 weeks and is 3-6 weeks for patients with severe or critical disease.”
Further WHO reports says:
Most people infected with COVID-19 virus have mild disease and recover. Approximately 80% of laboratory confirmed patients have had mild to moderate disease, which includes non-pneumonia and pneumonia cases, 13.8% have severe disease (dyspnea, respiratory frequency ≥30/minute, blood oxygen saturation ≤93%, PaO2/FiO2 ratio <300, and/or lung infiltrates >50% of the lung field within 24-48 hours) and 6.1% are critical (respiratory failure, septic shock, and/or multiple organ dysfunction/failure). Asymptomatic infection has been reported, but the majority of the relatively rare cases who are asymptomatic on the date of identification/report went on to develop disease. The proportion of truly asymptomatic infections is unclear but appears to be relatively rare and does not appear to be a major driver of transmission.
Individuals at highest risk for severe disease and death include people aged over 60 years and those with underlying conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease and cancer. Disease in children appears to be relatively rare and mild with approximately 2.4% of the total reported cases reported amongst individuals aged under 19 years. A very small proportion of those aged under 19 years have developed severe (2.5%) or critical disease (0.2%).
As of 20 February, 2114 of the 55,924 laboratory confirmed cases have died (crude fatality ratio [CFR2] 3.8%) (note: at least some of whom were identified using a case definition that included pulmonary disease). The overall CFR varies by location and intensity of transmission (i.e. 5.8% in Wuhan vs. 0.7% in other areas in China). In China, the overall CFR was higher in the early stages of the outbreak (17.3% for cases with symptom onset from 1- 10 January) and has reduced over time to 0.7% for patients with symptom onset after 1
February (Figure 4). The Joint Mission noted that the standard of care has evolved over the course of the outbreak.
Read more at WHO Report.